The 21st century has been bad news for proponents of limited government. Bush was a big spender, Obama was a big spender, Trump was a big spender, and now Biden also wants to buy votes with other people’s money.
That’s the bad news.
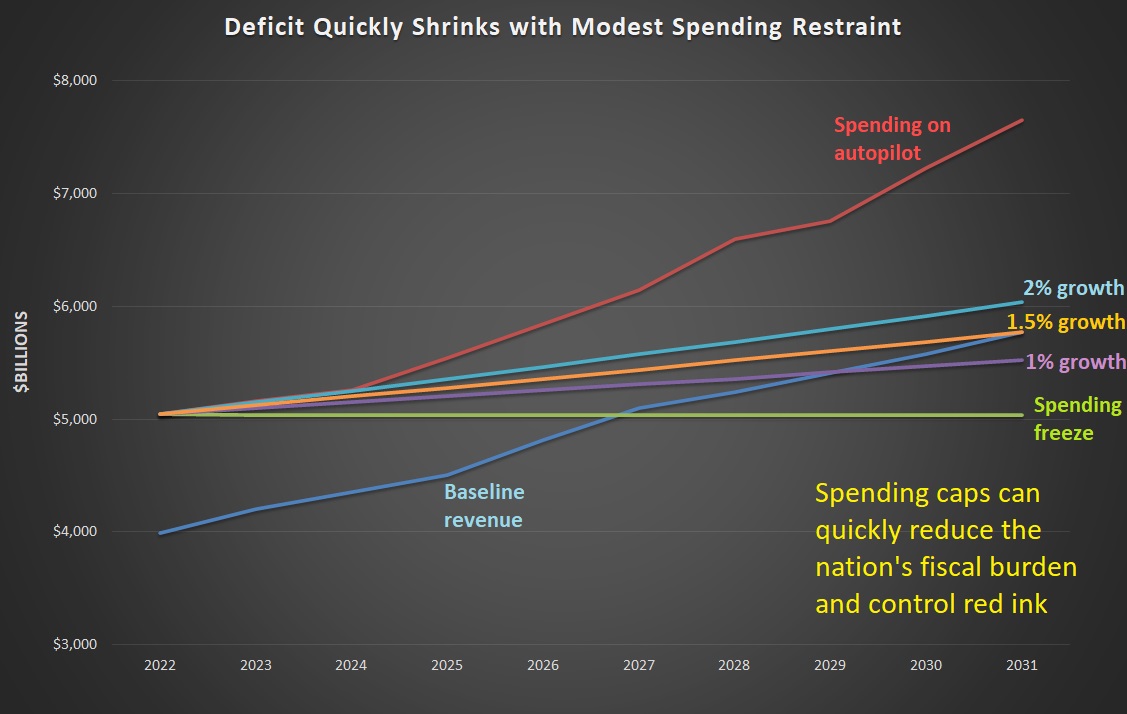
The good news is that there is still a simple solution to America’s fiscal problems. According to the just-released Budget and Economic Outlook from the Congressional Budget Office, tax revenues will grow by an average of 4.2 percent over the next decade. So we can make progress, as illustrated by this chart, if there’s some sort of spending cap so that outlays grow at a slower pace.
The ideal fiscal goal should be reducing the size of government, ideally down to the level envisioned by America’s Founders.
But even if we have more modest aspirations (avoiding future tax increases, avoiding a future debt crisis), it’s worth noting how modest spending restraint generates powerful results in a short period of time. And the figures in the chart assume the spending restraint doesn’t even start until the 2023 fiscal year.
The main takeaway is that the budget could be balanced by 2031 if spending grows by 1.5 percent per year.
But progress is possible so long as the cap limits spending so that it grows by less than 4.2 percent annually. The greater the restraint, of course, the quicker the progress.
In other words, there’s no need to capitulate to tax increases (which, in any event, almost certainly would make a bad situation worse).
P.S. The solution to our fiscal problem is simple, but that doesn’t mean it will be easy. Long-run spending restraint inevitably will require genuine reform to deal with the entitlement crisis. Given the insights of “public choice” theory, it will be a challenge to find politicians willing to save the nation.
P.P.S. Here are real-world examples of nations that made rapid progress with spending restraint.
P.P.P.S. Switzerland and Hong Kong (as well as Colorado) have constitutional spending caps, which would be the ideal approach.
There was no interest in fiscal restraint after 9/11. Nor was there during the Great Recession. Nor has there been during the pandemic. The only way to get closer to balancing the budget (I doubt it will be balanced in the lifetime of anyone reading this) is, as Mitchell points out, mandatory, as in constitutional, spending restraint.
Leave a comment